Deformed arthrosis of knee joint is a polyetiological disease. This means that there are many reasons for its development. In some cases, when the most dominant cause can be allocated, gonarthrosis is called secondary. In the event that a clear cause is not determined, the diagnosis of primary or idiopathic arthrosis of knee joint is established.

- Osteoarthritis of deformation of the medial part of the femoral bore articulation;
- Osteoarthritis of deformation of the side of the femoral Bore joint;
- DEFERRED ARTROSIS OF THE DELICIOUS ARTICULATION OF FEMORAL.
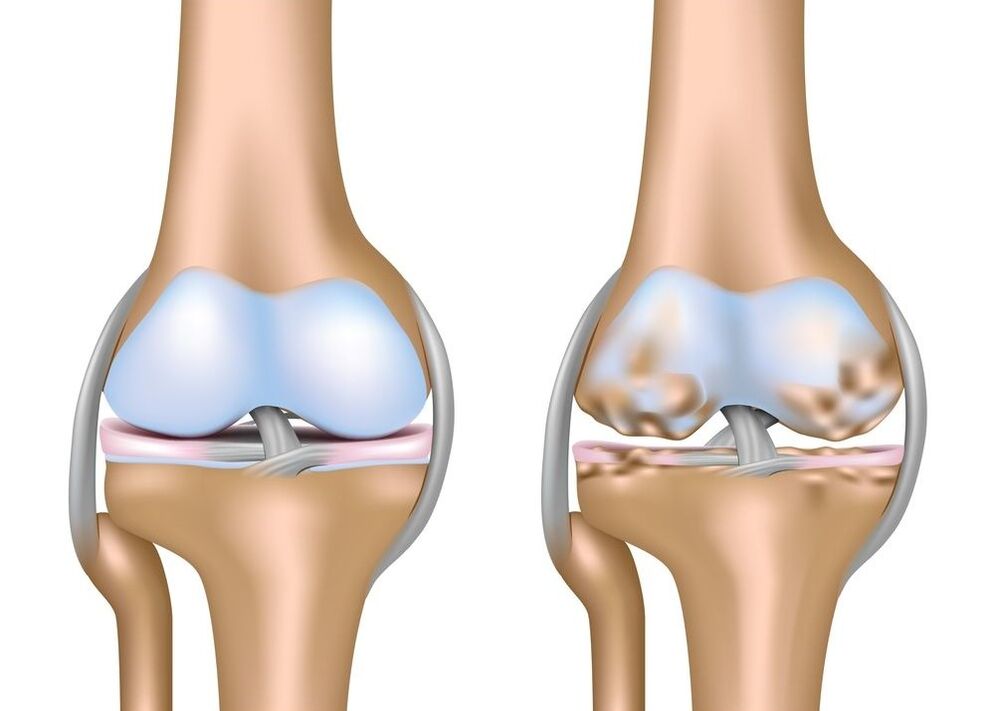
Normally, the destruction of joint cartilage occurs in the process of physiological withers throughout the organism, that is, during aging. The pathological destruction of cartilage is considered when it occurs before time or a more intense pace. The Middle Ages, in which, on a completely legitimate base, the first signs of cartilage degeneration can manifest is a period of 40 to 50 years. With deforming arthrosis, the disease debuts in childhood with the first manifestations of 16 to 18 years and, in some cases, even sooner. However, this is not a reason to despair.
The mechanism of disease development is a vicious circle in which the final links launch the initial and so on to infinity. However, each round of this circle exacerbates the condition of the cartilage and leads to the progression of the disease and so on. In the case of primary gonarthrosis, the reason that throws a vicious circle is unknown. However, their subsequent bonds are carefully studied in order to influence them and decrease the progression of the disease.
Deformed arthrosis develops approximately as follows. The daily joint cartilage of the knee joint experiences thousands of shocks that they are forced to depreciate so as not to harm the most proposed structures of the human body, such as internal organs and brain. Over time, due to concussions data, microscopic cracks are formed in the cloudy layer, which also after a certain period of time are filled with synovial fluid and become microdistas. Neighbor microdists tend to unite and the formation of larger cysts.
Increasing the size of corneal space cysts gradually begins by squeezing blood capillaries that feed the cartilage tissue on the bone side. The supply of oxygen and substances needed to maintain vital activity worsen, which leads to a slower synthesis of type 2 collagen.
Cartilage transport leads to two negative consequences. Firstly, this leads to a deterioration in depreciation properties and a more intensive formation of new microcrack in the subsidiary layer. Secondly, due to cartilage compression, its density increases, which adversely affects the second mechanism of its nutrition through the diffusion of synovial fluid in the thickness of the cartilage tissue.
However, on the scale of the whole body, the destruction of joint cartilage does not go unnoticed. As a compensatory reaction in the focus of cartilage washing, the activity of chondroblasts - young cells synthesizing the new cartilage tissue increases. However, this compensatory mechanism is imperfect, and its imperfection lies in the fact that most of the cartilage tissue is formed not at the place of greater cartilage destruction, but where cartilage does not experience loads.
As a result, cone -shaped cartilage growths are formed along the edges of the joint - Condoophytes. These chondroophytes do not manifest clinically until ossification processes begin in them. Okreteen, chlorophytes hardens and transform themselves, which are called peaks of ordinary people. As a rule, the appearance of peaks is always accompanied by the occurrence of pain and the development of inflammation in the joint. This is due to the fact that osteophytes during joint movement touch the cartilage tissue and the synovial shell, damaging -mechanically.
As a result, each complication of deformed arthrosis leads to the acceleration of the progression of pathological changes in the cartilage. However, knowing the mechanism for the development of gonarthrosis, some of its bonds can be successfully affected in order to slow down and improve a long -term forecast.
Secondary gonarthrosis differs from the main one, as the main reason is known, which launched a vicious circle of articular cartilage destruction. The additional course of the disease occurs in the same way as in primary gonarthrosis, with the peculiarity that the disease is constantly aggravated by the effect of negative factors associated with the underlying disease. For this reason, the course of secondary knee articulation arthrosis, as a rule, is more aggressive.
- lesions (acute and chronic);
- Congenital deformation of varus or valgus from the lower ends;
- Congenital shortening of one of the lower ends;
- knee joint hypermobility syndrome;
- congenital knee joint dysplasia;
- chondrocalcinosis;
- osteomyelitis;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- acromegaly;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- hypothyroidism;
- Fraud, etc.
Post -traumatic deformation arthrosis is divided into sharp and chronic. The acute form of the disease develops after a severe injury, more often -
, which occurs or partially extends to the joint part of the bone. The chronic form of the disease develops longer and is, as a rule, with frequent and light injuries in the joint. Such conditions are created by builders, road workers, engines, etc.
In acute gonarthrosis, the mechanism of the disease is associated with serious inflammatory changes in the joint cavity, namely, with lympostase, increased pressure in the joint cavity and a change in synovial fluid composition. Excessive acceleration of the growth of new cartilage tissues leads to joint surface deformation at the fracture site and osteophyte growth.
In chronic gonarthrosis, a severe inflammatory process is not observed, however, the frequent and intensive load on the cartilage tissue leads to its rapid compression, the formation of micro -size and the deterioration of the nutrient cartilage supply, both on the bone side and the joint gap.
People with this pathology can be found quite often. Its essence is to change the shape of the legs. With varied deformation, the legs are arched out on a horizontal plane. In other words, among the patient's legs, space is more than in healthy people. With the deformation of Valgus, the legs have a shape in the shape of X when the knees are in contact with each other. Both pathologies can be genetically programmed and developing throughout life due to fractures from the lower extremities.
In both cases, the load on one sides of the knee joint increases, with the deformation of varus - on side sides and valgus deformation - on the medial sides. Due to the fact that the same weight of the patient presses in a smaller area, the premature washing occurs of the cartilage, accompanied by inflammation, pain and morning stiffness.
Congenital shortening of one leg is a consequence of anomalies or may develop a few years after birth as a consequence of birth injury. As in the previous case, there is an unequal weight distribution and the normal leg assumes a large load. As a result, the joint cartilage of the healthy leg knee joint undergoes structural changes that lead to deforming arthrosis.
This pathological condition is not a disease, but it may very well bring it to it. This syndrome means excessive mobility of the ligament apparatus and consistent, in which joint joint movement within the normal axes can increase significantly. These patients almost never suspect that they have this feature, as they live with it all their lives and believe that other people also work the same way.
A sign of knee joint hypersmore is the formation of a stupid angle between the thigh front surfaces and the leg with the maximum leg straightening. In other words, the knees are bending, and the legs take a burning shape. In addition, these patients can easily reach the forearm with the thumb, reach the head of the legs and in principle have congenital flexibility.
Knee joint arthrosis symptoms
At the early stage of development, pathology is manifested by knee pain, moderately expressed and emerging while moving when moving through the stages.
An unpleasant symptom may appear if a person spends a lot of time standing or trying to rise after being in a long time.
At rest, health usually improves.
Intense severe pain comes spontaneously.
Most patients previously had prolonged discomfort during physical activity and when they walked. In this case, growing pain may be the main sign of the development of gonarthrosis.
The disease develops gradually for several months or years, when it is not yet visible deformation and intense pain. But during this period, discomfort in the knees, which occurs from time to time.
Remember, the sooner you consult a doctor, the easier and more successful the treatment will pass.
Not to be a visit to an expert, awaiting irreversible consequences. Take measures as soon as you notice the symptoms of the disease.
The obvious signs of knee joint arthrosis begin to manifest as the structure of cartilage shells, a decrease in synovial fluid production and articular harm damage. In the early stage of increased pathological changes, as a rule, there are no pronounced symptoms, but at the same time a slight stiffness may be present in the morning.
When pronounced and various symptoms appear, arthrosis, as a rule, is already in the late stage of its development. At this point, there is already serious damage to knee joint structures, so the disease enters the acute phase. The characteristic manifestations of the acute period of arthrosis development include:
- Increased pain;
- Change of march;
- Claudication;
- crispy when moving;
- Soft tissue swelling;
- an increase in the knee due to fluid accumulation;
- Limiting articulation mobility.
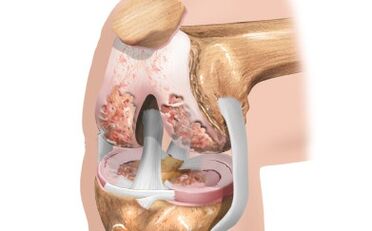
When knee arthrosis develops, symptoms can grow enough, but when the disease is a transition to the last stage of manifestation of a joint disorder, the quality of life significantly reduces the quality of life.
- The synovial shell against the bottom of damage to joint surfaces begins to be inflamed, which leads to a violation of the mobility of the entire articulation.
- Any movement with a damaged articulation can be very painful.
- In palpation, a significant increase in local body temperature is observed.
- As a rule, the effective treatment of knee articulation arthrosis with conservative methods is possible only at the early stage of disease development.
- Thus, when signs of the disease appear, consult a doctor for consultation.
In the development of a condition such as knee arthrosis, symptoms and treatment are interconnected, because if in the early stages of disease development, joint surfaces can still be completely restored and improved by local metabolism, then the later stages that drug treatment of knee usually does not have a positive effect, since cartilage.
Arthrosis of the 1st degree proceeds almost without visible symptoms. This phase of development is characterized by:
- fatigue in the legs;
- A slight decrease in mobility, which is usually observed immediately after sleep.
The symptoms of pain, if and occur, manifest in a slight degree. At this point, knee arthrosis looks at the root x in the form of small swelling in the cartilage tissue and the surface of the bones.
With the articulation of the 2nd degree knee articulation, the symptoms are more pronounced. The pain already arises from the minimum load or immediately after it. In the affected part of the leg, the pain is caused by almost any movement. After a very long rest, it usually goes completely. However, the next physical actions immediately cause pain.
Approximately in the second stage of disease development, pain sensations are added:
- crispy knee joint during movements;
- A reduced opportunity from bastard to leg normally in the knee;
- Change of joint bones;
- Progressive synovitis.
A crisis of artransciracira from the joints, as a rule, is almost little audible, but with the course of the disease, it becomes very high and distinct. When trying to fold the leg in the knee, acute pain occurs. In some cases, this is possible only for a 90 degree corner and then with difficulty and overcoming the pain. The change in the shape of the joint also becomes obvious, which is also aggravated by the accumulation of pathological fluid in it.
The characteristics characteristics of the third degree of arthrosis are severe pain that are independent of quantity, the intensity of physical activity. The articulation bothers a person even at night, this causes significant drawbacks.
Radiography can show global changes in cartilage, joint surface, non -characteristic growths. The curvature in the form of O or X shaped leads a person to deficiency. These are the consequences that cartilage tissue has already used and bone tissue has entered the "movement. "
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative-distribution disease, in which cartilage destruction and joint is deformed. Signs of the disease are severe pain, limb deformation, uneven distribution of loading in the bone muscle system, the development of complications and a significant decrease in mobility to the patient's disability.



















